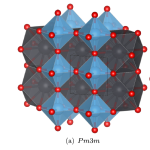
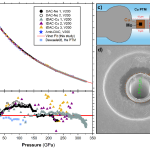
Ferroelectrics are very useful materials that interact strongly with electric fields, and have revolutionized, for only one example, medical ultrasound. New ferroelectrics have led to hand-held medical scanners, like in Star Trek, and have played significant role in increasing survival rates for battlefield casualties, lower infant mortality, and safety of the oceans through SONAR. In order to improve ferroelectrics, scientists must understand them. Whereas varying temperature or chemistry lead to complex changes in properties, applying pressure should be simpler to understand, as it… more
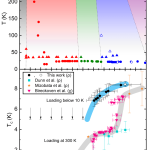
The superconducting and structural properties of elemental strontium metal were examined under pressures up to 60 GPa at low temperatures and high pressures. Applying pressure at low temperatures reveals differences in superconducting and structural phases compared to previous reports obtained under room-temperature compression. Notably, the superconducting critical temperature exhibits a twofold increase within the pressure range of 35–42 GPa when compressed at low temperatures. This is different when compared to cooling after a room-temperature compression. Above 42 GPa, the transition… more
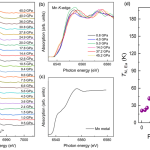
EuMnSb2 is a unique Dirac candidate compound with dual magnetic orders and a sizable coupling between the magnetic Mn and Eu sublattices. Earlier studies, through the application of an external magnetic field, have shown that the strongly coupled Eu magnetism and charge transport enable the magnetic control of topological quasiparticles. Motivated by this strong tunability, researchers led by Wenli Bi’s group at the University of Alabama at Birmingham applied external pressure to EuMnSb2 and systematically investigated the magnetic state, valence states of both Eu and Mn sublattices… more
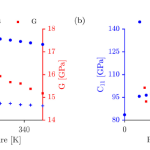
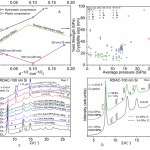
Researchers from Los Alamos National Laboratory recently reported on the development and validation of a multi-phase strength model for tin. This work supported a multi-year Tri-NNSA Lab initiative focused on the development of multi-phase strength models for metals and leveraged a wide range of experimental techniques with platforms spanning the full range from static to shock compression. Essential inputs to strength models are accurate and precise values for the shear modulus and its pressure derivative. In this work, these parameters were determined to ~5 GPa using… more
The toroidal diamond-anvil cell (tDAC) can routinely achieve pressures under static compression above 300 GPa, but accurate equations of state (EoS) measurements of materials to these conditions remains limited. To obtain high-quality EoS data, samples must be compressed in a soft pressure-transmitting medium (PTM) to provide a nearly isotropic compression environment, but the small tDAC sample chamber (~4 – 6 µm diameter) presents a great challenge for embedding micron-sized samples in a soft PTM. In a paper recently published in the Journal of Applied Physics as an Editor’s Pick,… more
Researchers from Iowa State University and HPCAT recently performed measurements on silicon using the novel rotational diamond anvil cell and found that shear and non-hydrostatic compression results in formation of Si-II at lower pressures and at ambient temperature. This study spearheaded by long-time HPCAT user, Prof. Valery Levitas (Anson Marston Distinguished Professor in Engineering and Murray Harpole Chair in Engineering at Iowa State University), was recently published in Nature Communications.
Traditional pressure and stress-induced phase transitions (PTs)… more
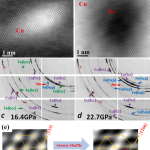
Department of Energy, NNSA Center of Excellence CAMCSE researchers have published their latest research in Scientific Reports detailing a high-resolution electron microscopy study on a pressure-treated 3-D printed super alloy known for its unusually high strength and high ductility.
The published study was led by UAB and includes participants from the University of Massachusetts-Amherst, the University of California-Irvine, and the University of Notre Dame. The real secret behind superlative mechanical properties of 3-D printed super alloys is the nanostructure… more
Improvement of alloys opens fundamentally new technical opportunities. Additive manufacturing is a powerful tool to make finely tuned alloys with tailored, previously unattainable combinations of properties. Application of high pressure puts the materials under a great deal of strain, and potentially reveals unexpected combinations of plastic, elastic deformations and atomic rearrangements. Researchers from University of Michigan, LLNL and ANL used the U.S. Department of Energy's Advanced Photon Source to look at an alloy of copper (Cu) and iron (Fe) under extremely high… more